What Is The Standard Deviation Of Any Z-distribution
1 bc any variate is a standard normal variate when it follows a normal distribution with Mean0 and standard deviation1. Z score 800-700 180.
If a normal distribution has a mean of 180 and a standard.

What is the standard deviation of any z-distribution. The study revealed that the spending distribution is approximately normally distributed with a mean of 411 and a standard deviation of 137. Values on the Z- distribution are called z -values z- scores or standard scores. If your Z-score distribution is based on the sample mean and sample standard deviation then the mean and standard deviation of the Z-score distribution will equal zero and one respectively.
Z Score Observed Value Mean of the Samplestandard deviation. The standard normal distribution is centered at zero and the degree to which a given measurement deviates from the mean is given by the standard deviation. A z-score equal to -2 signifies 2 standard deviations less than the mean.
If the number of elements in the set is large about 68 of the elements have a z-score between -1 and 1. This is the probability between 560 and -1 470. Match the variables to their description.
Once we have the Z Score which was derived through the Z Score formula we can now go to the next part which is understanding how to read the Z Table and map the value of the Z Score weve got using it. The standard normal distribution is a normal distribution with a mean of zero and standard deviation of 1. Of z-scores is zero and the standard deviation is 1.
The mean weight of a sample of bags of potato chips is 55 ounces and the standard deviation is 02 ounces. Z score x . When any distribution with any mean or standard deviation is transformed into z-scores the resulting distribution will always have a always have a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1.
Where x is the raw score is the population mean and is the population standard deviation. The average score on an IQ test is 110 and the standard deviation is 10 grams. So thats why transforming any variable into standard normal variable changes the standard deviation of.
The graph of the z-score distribution always has the same shape as the original distribution of sample values. About 95 have a z-score between -2 and 2 and about 99 have a z-score between -3 and 3. After the transformation what is the standard deviation for the sample of z-scores.
The formula for converting a normally distributed random variable X to a z-value is z XX-. It occurs when a normal random variable has a mean equal to zero and a standard deviation equal to one. In other wordsthe 25 th percentile is less than the mean by 0664 times the standard deviation.
By interpolationwe can get the z score for p 025 which corresponds to 25th percentitileas -0663796918. Z score 056. The random variable of a standard normal distribution is known as the standard score or a z-score.
Suppose random variable X has a normal distribution with a mean of 982 and the standard deviation of 32 find Px 99. The SND allows researchers to calculate the probability of randomly obtaining a score from the distribution ie. The Standard Normal Distribution The standard normal distribution is one of the forms of the normal distribution.
A z-score equal to -1 represents an element which is 1 standard deviation less than the mean. Therefore one standard deviation of the raw score whatever raw value this is converts into 1 z-score unit. The standard deviation of any SND always 1.
The sum of the squared z-scores is always equal to the number of z-score values. A z-value represents the number of standard deviations that a particular value lies above or below the mean. If mean is m standard deviation is sZ -066378618-ms relates to 25 th percentile.
For example z 1 on the Z- distribution represents a value that is 1 standard deviation above the mean. What is the z-value of a bag. The standard deviation of the z-scores is always 1.
What is the z-score for this problem. The z-score has numerous applications and can be used to perform a z-test calculate prediction intervals process control applications comparison of scores on different scales and more.

Standard Normal Table Area Under The Normal Curve Standard Deviation Normal Distribution Statistics Normal Distribution

Serving Our Patients By Studying Our Numbers Normal Distribution Standard Deviation Z Distribution

How To Calculate A Sample Standard Deviation Statistics Math Standard Deviation Studying Math

Standard Scores Iq Chart And Standard Deviation Z Scores Stanines Percentiles Sat Act Iq Standard Deviation Statistics Math Ap Psychology

Statistics 101 A Tour Of The Normal Distribution Normal Distribution Social Science Research Speech And Language

Normal Curve Distribution Of Iq Scores Normal Distribution Psychology Resources Bell Curve

Normal Distribution Normal Distribution Distribution Statistics Cheat Sheet

Removing Outliers Using Standard Deviation In Python Standard Deviation Normal Distribution Simple Definition

How To Read A Z Score Table To Compute Probability Normal Distribution Statistics Math Data Science Learning

A Comparison Of The Mean Median And Mode Statistics Math Ap Statistics Math Formulas
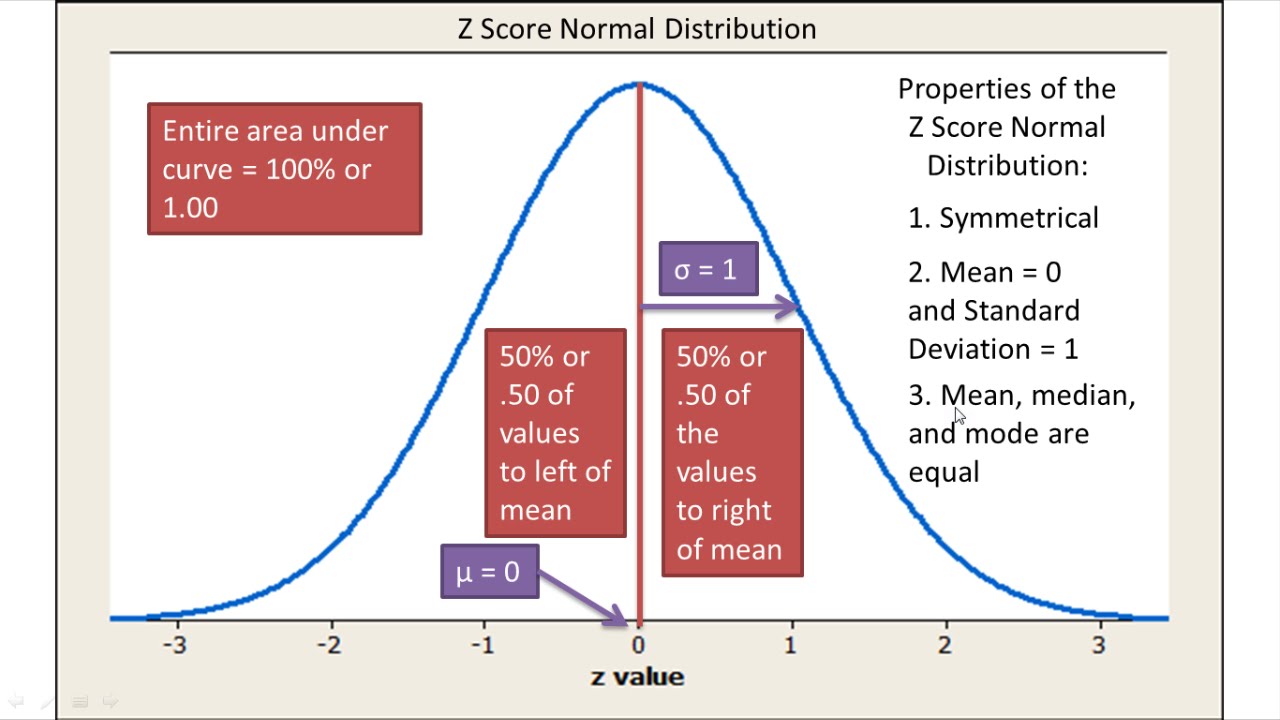
Normal Distribution And Z Scores Explained Introductory Statistics Normal Distribution Statistics Math Statistics Notes

Calculate Probability Of A Range Using Z Score Normal Distribution Statistics Math Data Science Learning

Lab 8 Z Score And Normal Distribution Normal Distribution Psychological Theories Applied Science

Normal Distribution Normal Distribution Data Science Learning Standard Deviation

Why Memorize When You Can Pin Normal Distribution And Scales Standard Score Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia Normal Distribution Standard Deviation Z Distribution

Statistics Math Math Formulas Standard Deviation

Calculate Probabilities With A Standard Normal Distribution Table Normal Distribution Probability Distribution

Standard Deviation Approximately 68 Of All Observations From Repeated Samples Would Fall Within One Standard Statistics Math Medical Math Standard Deviation


Post a Comment for "What Is The Standard Deviation Of Any Z-distribution"